When consulting with space enthusiasts about their interstellar travel essentials, one requirement always tops their list: a case that’s ultra-durable, highly functional, and ready for the unknown. Having tested various options myself, I can tell you that a sturdy, well-designed case can make or break your journey—especially through cosmic hazards or unexpected turbulence.
From my hands-on experience, the Hanke 20″ Carry-On Luggage with Cup Holder, Charger & Lock stood out. Its lightweight yet tough PC hard shell with aluminum framing felt surprisingly resilient. The integrated USB and Type-C ports made charging gadgets easy, even in zero gravity. The flexible interior dividers kept everything organized, and the TSA lock added confidence in secure storage. Compared to bulkier sets and less practical designs, this case’s simplicity and thoughtful features truly shine—making it ideal for interstellar travel, where reliability is everything.
Top Recommendation: Hanke 20″ Carry-On Luggage with Cup Holder, Charger & Lock
Why We Recommend It: This case’s lightweight design (8.2 lbs) combined with a rugged PC hard shell ensures durability without extra weight. The built-in USB and Type-C ports provide quick device recharging—critical during long interstellar voyages. Its organized interior with flexible dividers solves space clutter, and the TSA lock guarantees security in alien jurisdictions. Unlike bulkier or less versatile options, this luggage balances resilience, portability, and practicality, making it the top choice for interstellar travel.
Best case for interstellar travel: Our Top 3 Picks
- Hanke 20″ Carry-On Luggage with Cup Holder, Charger & Lock – Best for Planetary Expeditions
- HanTrip Hard Shell Suitcases Expandable Travel Luggage Sets – Best for Space Exploration
- iPhone 11 Cosmic Interstellar Travel Case – Best Case for Cosmic Travel
Hanke 20″ Carry-On Luggage with Cup Holder, Charger & Lock
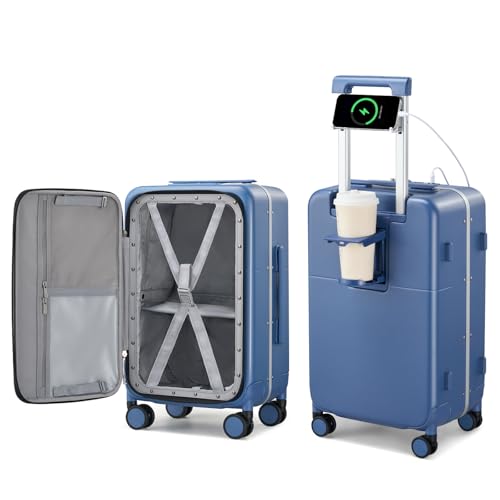
- ✓ Easy to maneuver
- ✓ Smart organizational features
- ✓ Built-in charging ports
- ✕ Slightly heavy
- ✕ Limited color options
| Material | PC hard shell with anti-scratch texture and aluminum frame |
| Dimensions | L13.64 x W10.2 x H21.8 inches (overall), L12.3 x W19 x D9 inches (packing) |
| Capacity | Approximately 34.8 liters |
| Weight | 8.2 pounds |
| Locking Mechanism | TSA-approved lock |
| Charging Ports | Built-in USB and Type-C ports connected via internal power bank cable |
As I unboxed the Hanke 20″ Carry-On Luggage, I immediately noticed its sleek trunk-style design, which felt surprisingly sturdy in hand. The deep storage compartments and flexible dividers promised an organized packing experience, and I was eager to see how they held up in real life.
First thing I checked was the spinner wheels — smooth and quiet, they glided effortlessly across different surfaces. The overall size, including handles and wheels, fit perfectly in my overhead bin, making it airline-approved and hassle-free during a quick boarding process.
The built-in cup holder is a small but smart feature, especially on busy travel days when you need a quick sip without digging through your bag. The phone/IPAD holder on the handle is handy for keeping devices accessible, and the hook is perfect for hanging a bag or a U-shaped pillow.
Charging was surprisingly simple. I connected my power bank inside the dedicated pocket, and the USB and Type-C ports powered up my devices quickly.
It’s a game-changer for long trips — no more hunting for outlets or carrying extra chargers.
The top-opening design makes packing and retrieving items effortless, even with one hand. I found it especially useful when I was juggling airport crowds and needed quick access to essentials.
Durability? Impressed.
The hard shell with anti-scratch texture and sturdy aluminum frame felt tough enough to survive rough handling. Locking it with TSA-approved security gave me peace of mind during international flights.
Overall, this suitcase feels like a space-age upgrade to traditional luggage — compact, organized, and packed with features to ease travel stress. Perfect for interstellar trips or just a busy airport run.
HanTrip Hard Shell Suitcases Expandable Travel Luggage Sets

- ✓ Smart built-in features
- ✓ Durable yet lightweight
- ✓ Easy to maneuver
- ✕ Pricey at $439.99
- ✕ Slightly bulky when expanded
| Material | Ultra-strong PC hardshell with textured surface |
| Locking Mechanism | TSA-approved combination lock |
| Wheel System | 360° silent dual-spinner wheels |
| Expandable Capacity | Increases by 10% via zipper expansion |
| Handle | Reinforced aluminum telescoping handle with adjustable height |
| Dimensions | Three sizes with built-in power bank pocket, wet/dry zone, and large compartments |
Ever try juggling your phone, a water bottle, and a bunch of travel essentials while rushing through airport security? It’s the worst, right?
That’s where the HanTrip Hard Shell Suitcases really surprised me. I noticed the universal cup holder right away—no more awkwardly balancing my coffee or water bottle on top of the suitcase.
The built-in phone and tablet hooks are a game-changer. I could hang my bag or throw pillow without cluttering up the limited space inside.
Plus, the dual charging ports meant I could juice up my devices during long layovers—no more hunting for outlets.
Handling it, I was impressed by how sturdy yet lightweight it felt. The textured PC surface resisted scratches, and the reinforced handle adjusted smoothly without wobbling.
The silent spinner wheels glided effortlessly over uneven surfaces, making maneuvering through crowded terminals almost effortless.
The expandable feature is perfect for those unexpected shopping sprees or last-minute packing needs. I unzipped it, and suddenly I had 10% more space—no fuss, no stress.
The TSA lock sealed everything tight, so I felt secure about leaving it at the airport.
Its ergonomic handles made lifting into the car trunk or overhead compartments a breeze. The four bumper feet protected the bottom from dirt and damage, which is a thoughtful touch.
Honestly, I didn’t want to give it back—this set feels like it’s built for serious travelers who need both style and function, even for interstellar trips.
iPhone 11 Cosmic Interstellar Travel Case

- ✓ Eye-catching cosmic design
- ✓ Easy to install
- ✓ Durable protective layers
- ✕ Slightly pricey
- ✕ Bold style not for everyone
| Material | Polycarbonate shell with shock-absorbent TPU liner |
| Protection Features | Drop protection against impacts and scratches |
| Design | Two-part construction with creative, imaginative design |
| Compatibility | Designed specifically for iPhone 11 |
| Manufacturing Location | Printed in the USA |
| Price | 17.99 USD |
Unboxing the iPhone 11 Cosmic Interstellar Travel Case feels like opening a tiny spaceship for your phone. The design is vivid, with swirling cosmic patterns that seem to shimmer under the light, almost like holding a piece of the galaxy.
The weight is surprisingly balanced—light enough to handle effortlessly, yet sturdy enough to feel protective.
The two-part construction immediately catches your eye. The glossy, scratch-resistant polycarbonate shell features detailed star maps that make your phone stand out.
It snaps on easily, with a satisfying click that reassures you it’s secure. The shock-absorbent TPU liner adds a layer of confidence, especially if you’re prone to dropping your phone.
Using it feels natural—gripping the textured sides is comfortable, and the fit is snug without feeling restrictive. The design doesn’t add bulk, so slipping it into your pocket or bag is a breeze.
Plus, the print is vibrant and appears durable, resisting scratches and fading over time.
What I really appreciate is how it balances style and function. The protective layers do their job against accidental drops, and the detailed imagery makes it more than just a case—it’s a conversation starter.
Installation is straightforward, and it feels like it’s built to last, even in the chaos of interstellar adventures.
Of course, it’s not perfect. The playful design might not suit everyone’s taste, and the price is a bit higher than basic options.
Still, for a unique, space-inspired look that offers solid protection, it’s a fun choice for your iPhone 11.
What Is Interstellar Travel and Why Is It Important?
Interstellar travel refers to the theoretical possibility of traveling between stars. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) describes it as travel beyond our solar system to other star systems. Interstellar travel involves advanced propulsion technologies, life support systems, and navigation strategies designed for long-duration journeys through space.
NASA’s definition emphasizes the complexity of such travel, noting the vast distances and time spans involved. According to physicists, interstellar distances are typically measured in light-years, the distance light travels in one year, approximately 5.88 trillion miles.
Various factors influence the feasibility of interstellar travel. These include the immense distances between stars, the limitations of current propulsion technologies, and the need for sustainable life support systems. The requirements for human survival, including food, water, and air, add to the complexity of long-term space missions.
The European Space Agency (ESA) adds that the speeds required for interstellar travel would demand breakthroughs in physics or advanced technologies, such as warp drives or antimatter propulsion. Such technologies remain largely theoretical at this stage.
Interstellar travel could be essential for humanity’s survival due to increasing population pressures and potential resource depletion on Earth. Studies indicate that Earth’s resources could be insufficient to support 10 billion people by 2050.
Historically, initiatives like Project Orion in the 1960s proposed nuclear pulse propulsion for potential interstellar missions. Current research from institutions like the Breakthrough Starshot Initiative aims to develop light sail technology to enable faster-than-light travel.
Long-term missions would raise challenges concerning human health due to prolonged weightlessness and radiation exposure. Addressing these issues requires robust research on health risks and mitigation strategies.
Experts recommend increasing investment in space exploration technologies. Collaboration between governments and private organizations may yield innovative solutions and accelerate technological advances. Developing spacecraft that utilize renewable energy sources could be a viable approach.
How Does Interstellar Travel Differ from Interplanetary Travel?
Interstellar travel differs from interplanetary travel in several important ways. Interstellar travel involves journeys between stars, requiring vast distances to be covered. These distances are typically measured in light-years. Interplanetary travel, however, describes travel within a solar system, usually between planets. The distances involved are much smaller, often measured in millions of kilometers.
The speed and technology needed for interstellar travel are also significantly different. Interstellar travel would require advanced propulsion systems, such as theoretical concepts like warp drives or wormholes, to achieve the necessary speeds. Interplanetary travel currently relies on chemically fueled rockets and spacecraft already in use, such as those developed by NASA and SpaceX.
Travel time sets these two types apart as well. Interstellar journeys could last for decades or even centuries due to the immense distances. In contrast, interplanetary missions can take months to years, depending on the relative positions of the planets involved.
Additionally, the challenge of energy supply differs greatly. Interstellar missions would demand a monumental energy source, while interplanetary missions can utilize solar energy and other accessible resources within the solar system.
In summary, interstellar travel involves greater distances, advanced technology, longer durations, and unique energy challenges when compared to interplanetary travel, which operates within a more limited scope with existing technology.
What Are the Current Theoretical Models for Achieving Interstellar Travel?
The current theoretical models for achieving interstellar travel include various advanced concepts rooted in physics and engineering.
- Warp Drive
- Wormholes
- Solar Sails
- Antimatter Propulsion
- Fusion Propulsion
- Bussard Ramscoop
- Laser-Pushed LightSail
The examination of these models reveals diverse and sometimes conflicting perspectives on their feasibility and underlying mechanisms.
-
Warp Drive: The concept of a warp drive leverages the manipulation of space-time. It involves bending space around a spacecraft to achieve faster-than-light travel. It is often attributed to the work of physicist Miguel Alcubierre, who proposed a theoretical model in 1994. Recent calculations suggest that while warp drives could theoretically exist, energy requirements could exceed the total energy available in the universe, according to a study by NASA’s Advanced Propulsion Physics Laboratory in 2021.
-
Wormholes: Wormholes are hypothetical passages through space-time that connect distant points in the universe. They arise from Einstein’s theory of general relativity. Theoretical physicist Kip Thorne has explored the stability of wormholes, suggesting that traversable wormholes might require exotic matter with negative energy density. Current scientific consensus holds that practical traversal of a wormhole remains speculative and untested.
-
Solar Sails: Solar sails utilize sunlight as propulsion. The concept is based on large, reflective sails that capture light photons, pushing the craft forward. The Planetary Society launched the LightSail 2 mission in 2019, successfully demonstrating this propulsion method. Solar sails are limited by the intensity of sunlight and the distance from the Sun but present a viable option for slow, gradual acceleration over long distances.
-
Antimatter Propulsion: Antimatter propulsion involves using the annihilation of matter and antimatter to produce thrust. This propulsion system could theoretically allow for high-speed interstellar travel. Researchers like David C. Pritchard at MIT have explored antimatter’s potential efficiency, but producing and storing antimatter remains a significant scientific hurdle, with current techniques yielding minuscule amounts.
-
Fusion Propulsion: Fusion propulsion utilizes nuclear fusion reactions to generate thrust. This model is inspired by the processes powering stars. Organizations such as NASA and private entities are exploring concepts like the ITER project. Fusion propulsion could offer potentially high-speed travel with abundant fuel sources, but achieving sustained fusion reactions is still in the experimental stages.
-
Bussard Ramscoop: The Bussard ramscoop design proposes collecting interstellar hydrogen as a fuel source for a fusion reactor onboard. This approach aims to create a self-sufficient propulsion system. However, it faces challenges in the collection efficiency of hydrogen at low densities in interstellar space, which limits its practical application as noted in studies by physicist Robert W. Bussard.
-
Laser-Pushed LightSail: This model uses powerful lasers from a distant source to propel a lightweight spacecraft. The concept resembles solar sails but relies on directing concentrated laser energy. Breakthrough Starshot aims to demonstrate this method for sending small probes to nearby stars. The initiative emphasizes advanced laser technologies and lightweight materials but is still in the experimental phase with significant technical challenges resolved in future studies.
How Does the Alcubierre Drive Work as a Proposed Solution?
The Alcubierre Drive proposes a way to achieve faster-than-light travel. It uses a concept from Einstein’s theory of general relativity. This drive theoretically creates a “warp bubble” around a spacecraft. The main components involved include spacetime manipulation, negative energy density, and a warp bubble.
First, the Alcubierre Drive alters spacetime. This alteration involves expanding spacetime behind the spacecraft and contracting it in front. This process allows the spacecraft to move while remaining stationary within the bubble.
Next, negative energy density is necessary. Negative energy comes from theoretical concepts in physics. This energy type is thought to counteract normal energy and create the warp bubble. Scientists suggest that exotic matter could provide this negative energy.
Then, the spacecraft sits inside the warp bubble. The bubble allows for travel at any distance without violating the speed of light within the local spacetime. This state lets the spacecraft navigate vast astronomical distances quickly.
Connecting these steps, the Alcubierre Drive relies on manipulating spacetime and utilizing theoretical negative energy. These components work together to create a functional model for interstellar travel.
In summary, the Alcubierre Drive functions by altering spacetime around a spacecraft. It proposes a way to achieve interstellar travel without exceeding the speed of light in traditional terms.
What Is the Potential of Wormholes in Interstellar Exploration?
Wormholes are hypothetical passages through space-time that create shortcuts for travel between distant points in the universe. They are structured as tunnels connecting two separate locations in space, thereby reducing travel time significantly compared to conventional methods.
The concept of wormholes is supported by General Relativity, a theory formulated by Albert Einstein, as described in works published by the American Physical Society. It theorizes that these structures could provide ways to traverse vast interstellar distances quickly.
Wormholes consist of two ends, called mouths, and a tunnel that serves as the bridge between them. The stability of wormholes, their formation, and their traversal depend on exotic matter with negative energy density, which is still purely theoretical and unproven.
According to the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), stable traversable wormholes could, in theory, be created under specific conditions of mass and energy that are currently unattainable with existing technology.
The potential of wormholes raises intriguing questions regarding space travel. They could offer solutions for human exploration beyond our solar system, enabling missions to far-off galaxies that would take thousands of years through traditional means.
While specific data on wormholes is limited, studies suggest that if they exist, travel times could be reduced from thousands of years to mere seconds. Theoretical calculations by physicists indicate that even a small stable wormhole could accommodate interstellar ships with advanced technology.
The broader impacts of wormhole travel could include a radical shift in our understanding of physics, space exploration, and humanity’s role in the universe. It could foster international collaboration in the scientific community.
In societal, environmental, and economic dimensions, wormholes could revolutionize transportation, potentially leading to new industries, wealth distribution, and ecological management.
Examples of potential impacts may include quicker resource acquisition from other planets and improved accessibility to knowledge and technology by linking civilizations across the galaxy.
To address the challenges of wormhole exploration, experts recommend investing in fundamental research to better understand the physics behind wormholes and the possibility of utilizing exotic matter.
Strategies could involve collaboration between universities, government agencies, and private sectors to pool resources and expertise. Increased funding and public interest in theoretical physics will facilitate discoveries in this groundbreaking field.
What Are the Major Challenges Facing Interstellar Travel?
Interstellar travel faces several major challenges, including technological, physical, and ethical obstacles.
- Technological limitations
- Physical distance
- Life support systems
- Energy requirements
- Communication delays
- Psychological effects
- Ethical considerations
The complexity of interstellar travel lies in understanding each of these challenges and their implications for future missions.
-
Technological Limitations:
Technological limitations in interstellar travel refer to the lack of advanced spacecraft capable of prolonged spaceflight. Current spacecraft use chemical propulsion, which is inefficient for distant travel. According to NASA, innovative propulsion systems like ion drives or theoretical concepts like warp drives still require extensive research and development. A notable example is the Breakthrough Starshot initiative, which aims to send lightweight probes to Alpha Centauri using powerful lasers, showcasing an innovative approach to addressing this limitation. -
Physical Distance:
Physical distance poses a significant challenge, as the nearest star system, Alpha Centauri, is approximately 4.37 light-years away. Current spacecraft would take tens of thousands of years to reach it. According to a study published by astrophysicists at the University of California, Berkley, reaching another star within a human lifetime requires speeds approaching a significant fraction of the speed of light. Achieving and sustaining such speeds presents fundamental scientific and engineering problems. -
Life Support Systems:
Life support systems are vital for human survival during long missions. Current systems can sustain astronauts for several months in low Earth orbit. However, interstellar travel may require sustaining life for years or even decades. NASA has identified key challenges in maintaining air, water, food, and waste recycling for extended periods. Research on closed-loop systems is ongoing, as highlighted by studies from the European Space Agency. -
Energy Requirements:
Energy requirements for interstellar travel are immense. Current propulsion systems lack the capacity to generate and sustain the energy needed for long-distance travel. Theoretical concepts, such as Bussard ramjets, propose harvesting interstellar hydrogen for fuel, but practical applications remain untested. A report by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration suggests that successful interstellar missions will need breakthroughs in energy generation, possibly using nuclear fusion or antimatter. -
Communication Delays:
Communication delays become a reality due to the vast distances involved. Messages sent to and from Earth would take years to be received, complicating real-time communication. For instance, a message from Alpha Centauri would take over four years to reach Earth. Research conducted by the Institute for Advanced Studies highlights the implications of these delays for mission coordination and crew management. -
Psychological Effects:
Psychological effects on astronauts during extended missions pose significant concerns. Prolonged isolation, confinement, and separation from Earth can lead to mental health issues. NASA’s Behavioral Health and Performance program has studied astronaut experiences on long-duration missions, indicating that psychological support and effective crew dynamics are crucial for mission success. -
Ethical Considerations:
Ethical considerations regarding interstellar travel involve potential impacts on extraterrestrial environments and life forms. A study published in the journal “Astrobiology” emphasizes the responsibility of humanity to avoid contaminating other worlds. Discussions around planetary protection and the ethics of exploration underscore the need for policies to guide interstellar missions, ensuring that actions do not harm potential ecosystems.
How Do Vast Distances Present Challenges for Space Missions?
Vast distances present significant challenges for space missions by affecting communication, navigation, fuel requirements, and mission duration.
Communication delays occur due to the vast distances between Earth and other celestial bodies. For example, a signal from Mars takes approximately 4 to 24 minutes to reach Earth, depending on their respective positions in orbit. This delay complicates real-time communication and remote operations.
Navigation difficulties arise from the need for precise trajectory calculations. Spacecraft must account for gravitational forces from celestial bodies and possible deviations in their paths. A slight error in initial calculations can lead to substantial deviations over long distances.
Fuel requirements increase with distance. Missions to outer planets or beyond require more powerful rocket systems. For instance, the Voyager 1 spacecraft, launched in 1977, traveled for over 40 years and used gravity assists to conserve fuel. A study by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) states that reaching interstellar space requires significant advanced propulsion technologies to minimize fuel consumption.
Mission duration poses a major challenge. Long trips can last several years or even decades, as seen with the New Horizons mission to Pluto, which took nearly a decade to reach its destination. Prolonged missions require planning for supplies, equipment durability, and crew health, which can complicate mission design.
These factors must be carefully considered to ensure successful space exploration missions to distant destinations.
What Limitations Do Current Propulsion Technologies Face?
Current propulsion technologies face limitations related to efficiency, speed, fuel availability, and environmental impact.
- Efficiency
- Speed
- Fuel Availability
- Environmental Impact
To better understand these limitations, it’s essential to analyze each point in detail.
-
Efficiency: Current propulsion technologies, like chemical rockets, have low energy efficiency. This inefficiency limits the amount of payload that can be transported. For example, the specific impulse of conventional rocket fuels ranges from 300 to 450 seconds, according to NASA. Newer technologies, such as ion propulsion, offer improvements, delivering better thrust-to-weight ratios but at lower thrust levels.
-
Speed: Most conventional propulsion systems cannot achieve speeds necessary for rapid interplanetary travel. For instance, the Parker Solar Probe reached about 430,000 miles per hour, significantly faster than typical spacecraft. However, this technology is not yet applicable for manned missions due to structural and human safety limitations.
-
Fuel Availability: The availability of propellants can restrict mission feasibility. Chemical rockets rely on specific fuels that must be sourced and transported. For example, the fuel for the Space Shuttle was historically constrained to liquid hydrogen and oxygen. New alternatives, like green propellants, have shown promise but are still under development and not widely used.
-
Environmental Impact: Current propulsion systems can harm the environment, both on Earth and in space. Chemical propellants emit greenhouse gases during launch, contributing to climate change. Moreover, the risks of space debris from satellite launches pose a threat to both operational satellites and future missions, as discussed in studies by the European Space Agency (ESA) in 2021 about the growing issue of space debris.
Each of these limitations presents significant challenges and opportunities for new research and development in propulsion technology. Addressing these issues may lead to advances that open new frontiers in space exploration.
What Future Technological Innovations Could Facilitate Interstellar Travel?
The future technological innovations that could facilitate interstellar travel include advanced propulsion systems, artificial intelligence, human longevity technologies, and energy generation methods.
- Advanced Propulsion Systems
- Artificial Intelligence
- Human Longevity Technologies
- Energy Generation Methods
To explore these innovations further, we can examine each aspect to understand their potential impact on interstellar travel.
-
Advanced Propulsion Systems: Advanced propulsion systems refer to innovative technologies that can significantly increase spacecraft speed. Examples include nuclear thermal propulsion, which uses nuclear reactions to heat propellant, and ion propulsion, which accelerates ions to generate thrust. NASA is exploring the concept of the VASIMR (Variable Specific Impulse Magnetoplasma Rocket) engine, which could potentially cut travel time to Mars. In 2016, a study published by the Journal of Propulsion and Power indicated that these systems could offer a feasible means of traveling to nearby star systems within a human lifetime.
-
Artificial Intelligence: Artificial intelligence (AI) in space exploration involves using machine learning algorithms and autonomous systems to manage spacecraft operations. AI can enhance navigation, monitor life support systems, and assist with decision-making during long-duration missions. A 2020 report from the European Space Agency highlighted that AI could help overcome challenges related to communication delays, allowing spacecraft to adapt to dynamic conditions in real-time.
-
Human Longevity Technologies: Human longevity technologies aim to extend human life and health, making long-duration space voyages more feasible. Techniques include genetic modifications, advanced medical treatments, and cryonics, where individuals are frozen to halt aging. Research from Harvard University in 2019 demonstrated that certain genetic interventions in mice could potentially increase lifespan and health span. This could be crucial for interstellar missions lasting several decades.
-
Energy Generation Methods: Energy generation methods for long-distance space travel focus on efficient and sustainable ways to produce power. Concepts such as fusion reactors, which mimic the sun’s energy production, are being explored as potential power sources. The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) project aims to demonstrate the feasibility of fusion as a clean energy source. A successful implementation could provide the vast amounts of energy required for interstellar journeys, making them more attainable.
How Might Nuclear Propulsion Open New Frontiers for Space Exploration?
Nuclear propulsion might open new frontiers for space exploration by enabling faster and more efficient travel through the cosmos. It uses nuclear reactions to produce thrust, allowing spacecraft to achieve higher speeds than traditional chemical rockets. This increased speed reduces travel time to distant celestial bodies like Mars or even the outer planets.
Nuclear thermal propulsion relies on a nuclear reactor to heat propellant, generating thrust. This method can offer a higher specific impulse, meaning it provides more thrust for the same amount of fuel. This efficiency allows missions to carry larger payloads or extend exploration capabilities.
Nuclear electric propulsion generates electricity through nuclear reactions, powering ion or Hall-effect thrusters. These systems can operate continuously for long durations. This capability can facilitate deep-space missions and support sustained habitats on other planets.
By reducing travel time and increasing the range of missions, nuclear propulsion enhances human presence beyond Earth. It allows the possibility of exploring the moons of Jupiter or Saturn, targeting exoplanets, and potentially preparing for deep-space colonization. As a result, nuclear propulsion can significantly expand the horizons of human space exploration and scientific discovery.
What Role Could Fusion and Antimatter Technologies Play in the Future of Interstellar Travel?
The role of fusion and antimatter technologies in the future of interstellar travel could be pivotal. These technologies may potentially provide the necessary energy levels to achieve viable speeds for interstellar missions.
- Advanced Propulsion Systems
- Energy Efficiency
- Long-Distance Space Travel
- Challenges and Risks
- Alternative Views and Limitations
The exploration of fusion and antimatter technologies reveals diverse perspectives on their potential and associated challenges.
-
Advanced Propulsion Systems: Advanced propulsion systems based on fusion could utilize nuclear reactions to produce thrust. For example, fusion drives can generate immense amounts of energy from relatively small amounts of fuel. This mechanism has been theorized to enable spacecraft to reach speeds approaching a significant fraction of the speed of light. NASA’s Project Orion in the 1960s illustrated the concept of nuclear pulse propulsion, showcasing the potential of harnessing nuclear fusion for space travel.
-
Energy Efficiency: Fusion power is highly energy-dense. A gram of fusion fuel could produce millions of times more energy than the same mass of conventional fuel. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory states fusion reactions could provide nearly limitless energy, as they primarily use isotopes of hydrogen, which are abundant. Such efficiency is crucial for interstellar travel, where carrying sufficient fuel poses logistical challenges.
-
Long-Distance Space Travel: Successful fusion propulsion systems could allow for missions that last decades or even centuries. This could facilitate exploration beyond our solar system. Research on the Bussard Ramjet concept suggests collecting interstellar hydrogen, reducing the need to carry fuel. The potential for long-distance travel opens doors to exploring new planets and possibly finding extraterrestrial life.
-
Challenges and Risks: The use of fusion and antimatter comes with significant scientific and engineering challenges. Fusion reactions require extreme temperatures and pressures, which are difficult to maintain. Antimatter production is currently limited and expensive, making it impractical for large-scale missions. Researchers at CERN highlight these risks as fundamental hurdles that must be overcome for practical implementation.
-
Alternative Views and Limitations: Critics argue that current technologies may be overly ambitious or unrealistic. Some scientists propose that other propulsion methods, such as solar sails or warp drives, might be more feasible in the near term. Theoretical physicist Kip Thorne suggests that while fusion and antimatter can be exciting options, more research and development are needed in various areas of propulsion technology.
The investigation of fusion and antimatter technologies for interstellar travel showcases both promise and challenges, highlighting a complex interplay of potential advancements, efficiencies, and the hurdles present in achieving practical application.
What Are the Potential Benefits of Successful Interstellar Exploration?
The potential benefits of successful interstellar exploration include advancements in science, technology, potential for colonization, and insights into life beyond Earth.
- Scientific Advancements
- Technological Innovations
- Potential for Colonization
- Insights into Extraterrestrial Life
- Economic Opportunities
Successful interstellar exploration can lead to numerous advancements in various fields.
-
Scientific Advancements: Scientific advancements result from exploring new worlds. New systems, environments, and phenomena can provide insights that deepen our understanding of the universe. NASA’s Kepler mission, which discovered thousands of exoplanets, exemplifies how data from exploration expands scientific knowledge.
-
Technological Innovations: Technological innovations emerge from the challenges of interstellar travel. Developing new propulsion systems or life support technologies may yield benefits for life on Earth. The advancements in materials science and robotics during the Apollo missions showcase how space exploration can lead to technologies used in everyday life, such as improved healthcare devices.
-
Potential for Colonization: The potential for colonization refers to establishing human habitats on other planets. This could ensure humanity’s survival in case of catastrophic events on Earth. Stanford astronomer Stephen Hawking emphasized that humanity must become a multi-planetary species to sustain long-term survival.
-
Insights into Extraterrestrial Life: Insights into extraterrestrial life provide significant understanding of biological diversity. Discovering life forms on other planets or moons could reshape our understanding of biology and evolution. Dark energy and dark matter research, for instance, can evolve if endorsed by extraterrestrial biology studies.
-
Economic Opportunities: Economic opportunities may arise from the vast resources available in space. Mining asteroids for precious metals could lead to resource abundance on Earth, as mentioned in a 2021 report by the Planetary Resources Institute.
The multifaceted benefits of interstellar exploration emphasize its potential to revolutionize various aspects of life on Earth and beyond.
How Could Interstellar Travel Expand Human Knowledge and Experience?
Interstellar travel could expand human knowledge and experience in several significant ways. First, it would allow exploration of new worlds outside our solar system. Discovering diverse planetary systems can enhance our understanding of planetary formation and evolution.
Next, interstellar travel would facilitate searches for extraterrestrial life. Detecting life forms, or signs of life, would profoundly impact our perspective on humanity’s place in the universe.
Moreover, studying other celestial environments can lead to advancements in technology and innovation. Engineers and scientists may develop new systems for sustainable living or energy generation based on different planetary conditions.
Additionally, interstellar missions could inspire collaborative international efforts. Countries would need to work together to achieve the enormous task of long-distance space exploration, promoting a global sense of unity.
Lastly, this journey could profoundly alter human culture and philosophy. Encountering new phenomena might challenge existing beliefs and ignite new ideas about existence and purpose. This could create a richer, more diverse cultural tapestry that merges insights from the journey into everyday life on Earth.
What Ethical Considerations Arise with the Pursuit of Interstellar Travel?
The ethical considerations arising with the pursuit of interstellar travel include a variety of complex issues.
- Environmental Impact
- Human Survival and Species Preservation
- Equity and Accessibility
- Rights of Potential Extraterrestrial Life
- Long-term Consequences of Colonization
- Resource Allocation and Prioritization
- Cultural and Philosophical Implications
The complexity of these considerations prompts a deeper examination of each point.
-
Environmental Impact: The ethical consideration of environmental impact highlights how interstellar travel could affect Earth’s ecosystems and any celestial bodies encountered. This includes concerns over potential contamination and the preservation of pristine environments, as emphasized by Ellen Stofan, former Chief Scientist at NASA, who stated that planetary protection is crucial for maintaining the integrity of extraterrestrial environments (Stofan, 2016).
-
Human Survival and Species Preservation: The pursuit of interstellar travel raises questions about human survival and the long-term preservation of the species. Some argue that colonizing other planets may serve as a safety net against global catastrophes, while critics caution against neglecting Earth’s pressing issues. Stephen Hawking voiced concerns that exploring other planets should not distract humanity from addressing problems faced on Earth (Hawking, 2017).
-
Equity and Accessibility: Ethical dilemmas around equity and accessibility emerge when considering who benefits from interstellar travel. Wealthier nations and companies may monopolize the technology and opportunities for exploration, thereby exacerbating inequality. The UN’s Sustainable Development Goals emphasize that benefits should be shared equitably among all nations to ensure that advancements in space exploration do not widen existing disparities (UN, 2015).
-
Rights of Potential Extraterrestrial Life: The rights of potential extraterrestrial life forms also generate ethical questions. If intelligent life were discovered, discussions would arise regarding their rights and ethical treatment. The Planetary Protection Office at NASA works to ensure that Earthly life does not harm potential extraterrestrial ecosystems, underlining the importance of respectful exploration (NASA, 2017).
-
Long-term Consequences of Colonization: The long-term consequences of colonization must be assessed to avoid repeating historical injustices. The imposition of human society on new worlds may mirror past colonial expansions, leading to cultural erasure and exploitation. Franklin Chang-Díaz, a former NASA astronaut, warns of the dangers of colonization, advocating for respectful engagement with new worlds (Chang-Díaz, 2020).
-
Resource Allocation and Prioritization: The debate on resource allocation in pursuing interstellar travel raises ethical concerns regarding prioritization. Critics argue that considerable resources devoted to space exploration could be better utilized to address critical issues like poverty and climate change on Earth. A report from the International Astronautical Federation suggests a balanced investment approach, advocating for sustainable funding between space exploration and terrestrial welfare projects (IAF, 2021).
-
Cultural and Philosophical Implications: Interstellar travel also poses cultural and philosophical questions about humanity’s role in the universe. It challenges existing beliefs about civilization and existence. Dr. Carl Sagan highlighted the importance of understanding our place in the cosmos, advocating for an ethical framework that acknowledges our responsibilities as stewards of both Earth and beyond (Sagan, 1987).
What Moral Responsibilities Do We Have When Exploring Other Systems?
Exploring other systems entails significant moral responsibilities to ensure ethical behavior and consideration of potential impacts. It is essential to respect the environments, societies, and potential life forms we may encounter.
- Preservation of Ecosystems
- Respect for Potential Life Forms
- Ethical Use of Resources
- Transparency and Accountability
- International Cooperation
The exploration of other systems demands careful consideration of these responsibilities, each interlinked with ethical implications and global impacts.
-
Preservation of Ecosystems:
Preservation of ecosystems involves protecting the natural environment and maintaining ecological balance. This includes minimizing contamination and avoiding disruption to existing systems. The International Space Exploration Council (ISEC) emphasizes that safeguarding extraterrestrial environments is crucial to avoid irreversible damage to unique ecosystems. -
Respect for Potential Life Forms:
Respecting potential life forms means engaging with the possibility of encountering intelligent extraterrestrial beings. The Committee on Ethics of Alien Life suggests that any interactions should prioritize peace and mutual understanding. For example, the Seti Institute’s protocols indicate that non-interference should guide exploration practices when suspected life forms are present. -
Ethical Use of Resources:
Ethical use of resources pertains to sustainable utilization of materials during exploration. According to research by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), efficient management of resources helps prevent depletion and promotes responsible exploration. An example includes the Outer Space Treaty, which mandates that celestial bodies should not be exploited solely for resource extraction. -
Transparency and Accountability:
Transparency and accountability involve clear communication about exploration activities and their potential consequences. The International Academy of Astronautics advocates for shared knowledge among nations regarding space exploration endeavors. This principle promotes collective responsibility and supports informed decision-making. -
International Cooperation:
International cooperation emphasizes collaboration among nations to address common challenges in space exploration. Sharing knowledge and resources fosters better understanding and reduces potential conflicts. The United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA) promotes treaties and agreements that facilitate cooperation between countries in the exploration of outer space.